Lymphedema, characterized by the swelling of limbs due to lymphatic system blockage, requires a multifaceted treatment approach to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The primary treatment for lymphedema is Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT), which includes four components:
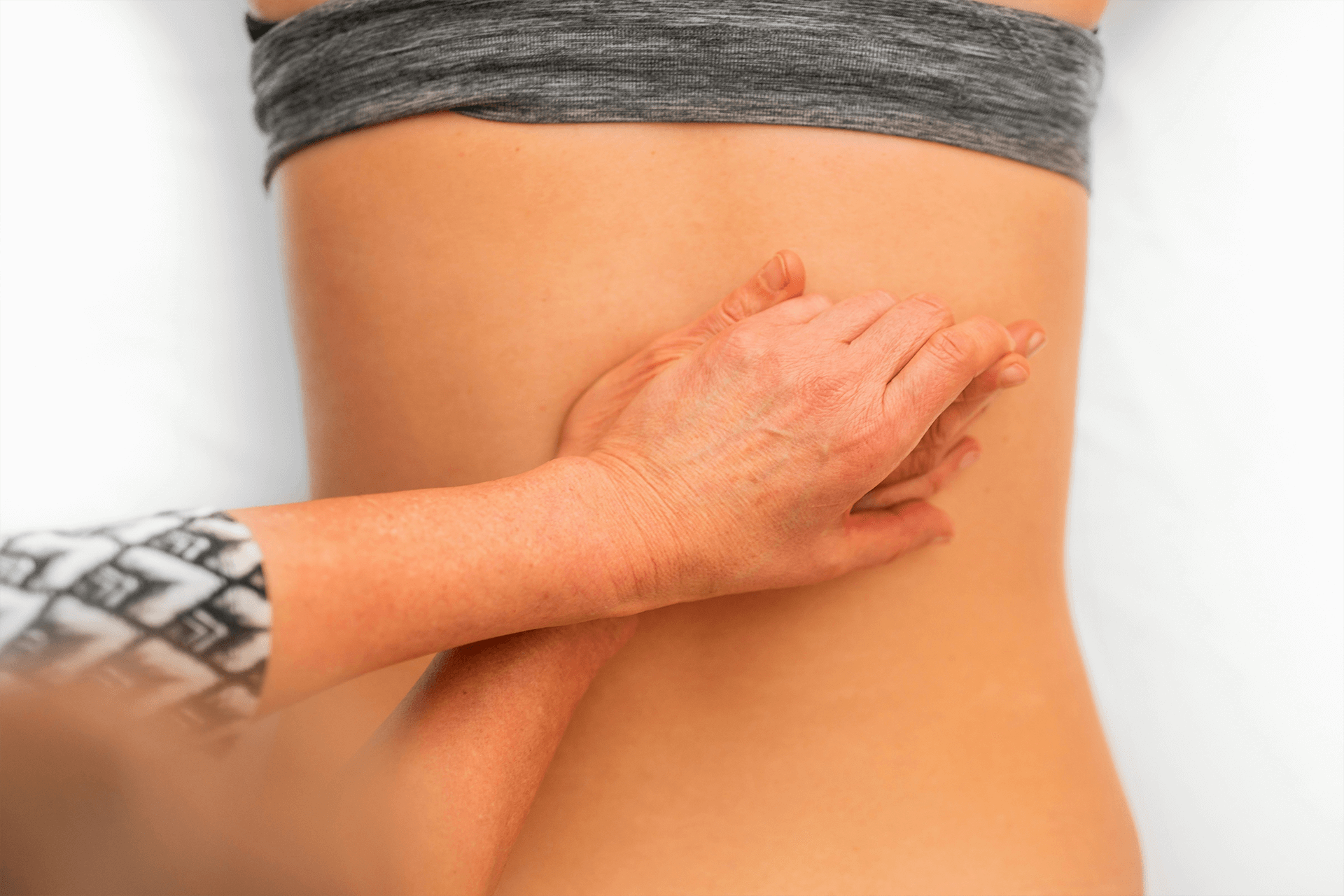
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD):
This is a gentle, massage-like technique designed to stimulate the lymphatic vessels and promote the flow of lymph fluid out of the affected limb. It is usually performed by a trained therapist.
Compression Therapy:
Using compression garments or bandages helps prevent fluid accumulation. These garments must be properly fitted and worn consistently. Bandaging is often used during the initial intensive phase of CDT, followed by custom-fitted compression garments.
Exercise:
Specific exercises can help improve lymphatic flow and maintain limb mobility. These exercises are typically low-impact and tailored to the patient’s condition, focusing on activating the muscles to aid lymph drainage.
Skin and Nail Care:
Good hygiene and skincare are crucial to prevent infections, which are common complications of lymphedema. Patients are advised to keep the skin clean and moisturized and to take precautions to avoid cuts and injuries.
In addition to CDT, other treatments may include:
Pneumatic Compression Devices:
These devices, which consist of a sleeve worn over the affected limb that inflates and deflates, can help reduce swelling by encouraging lymph fluid movement.
Medications:
While not a primary treatment, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat or prevent infections. Diuretics are generally not recommended as they do not effectively reduce lymphedema.
Surgical Options:
In severe cases, surgery may be considered. Procedures can include lymphatic bypass surgery, lymph node transfer, or liposuction to remove excess fat and fluid.
Patients are also encouraged to make lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, and wearing loose-fitting clothing to minimize constriction.
Overall, the goal of lymphedema treatment is to manage symptoms, reduce swelling, and improve the patient’s quality of life through a combination of therapeutic techniques and lifestyle modifications. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.